How Does A Water Softener Work
- The mineral tank’s dirt is removed during the backwash phase.
- Calcium and magnesium are replaced by sodium from the brine solution when the mineral tank is refilled, and these minerals are subsequently flushed down the drain.
- The brine tank is loaded and the mineral tank is rinsed with fresh water in the last step to prepare it for the next cycle.
It’s easy to overlook the significance of water in our daily lives.
In our houses, water serves as a tool — a fluid that transports materials from one location to another.
We obviously need it for our nutrition.
The fact that it is excellent at retaining things, whether by suspending them or dissolving them, is one of the reasons it does its task successfully.
But water doesn’t come with a user’s guide as other gadgets do.
If it did, you would be aware of the reasons why your dishes, which you believed to be clean, have stains after they are dried, your shower water leaves a film on everything it touches, and your plumbing system has become blocked with what you believed to be clean water.
- The mineral tank’s dirt is removed during the backwash phase.
- Calcium and magnesium are replaced by sodium from the brine solution and then flushed down the drain after being replaced in the mineral tank.
- The brine tank is loaded and the mineral tank is rinsed with fresh water in the last step to prepare it for the next cycle.
The Problem Is The Solution
Water takes up soluble particles of everything it goes through while in the earth.
While this might signal a contaminant that renders the water unsafe for consumption, it often only indicates that the water includes minerals that can be found in the ground.
Of these, calcium and magnesium are particularly significant since they have an impact on how well our houses’ water functions.
Our water is made hard by these minerals.
The efficacy of soaps and detergents is one impact of hard water.
Minerals and soap mix to produce a coagulated soap curd instead of the soap totally dissolving.
More is needed since less soap dissolves.
Additionally, the greasy, insoluble curd remains; it adheres to the skin and may even prevent cleaning.
Hair after a wash seems lifeless and drab.
Things aren’t much better with the laundry.
While your garments are being cleaned in your automated washing machine, the soap curd may find its way into them.
This may stiffen and roughen the cloth as well as keep dirt trapped in the fibers.
Insoluble soap deposits create stains on everything you wash, including your dishes and the family vehicle, and a soap film will accumulate in your bath and shower, in addition to interfering with the actual washing process.
Your plumbing system’s vulnerability to the effects of hard water is another cause to be worried.
Pipe deposits made of calcium and magnesium may lessen the flow of water to faucets and appliances.
These minerals cause a scale accumulation in water heaters that shortens the heater’s lifespan and efficiency.
The Cure
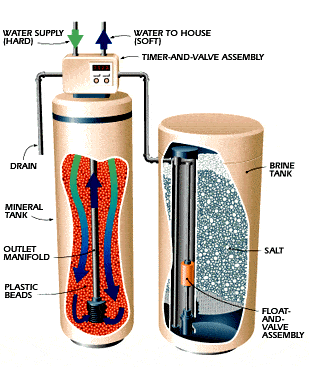
Positively charged calcium and magnesium ions are lost by water flowing through the mineral tank to negatively charged plastic beads.
The mineral tank is flushed with sodium ions instead of calcium and magnesium ions using the brine tank’s salt solution.
The mineral tank’s top meter controls the frequency of recharge cycles.
Each stage of the regeneration cycle’s water flow is routed via the valve assembly.
Eliminating the calcium and magnesium is the problem’s remedy.
Although there are chemical treatments that may do this, a water softener is the most often used solution.
A conventional water softener is a mechanical device connected to your home’s water supply system through plumbing.
All water softeners work on the same premise: They exchange the minerals for another substance, often sodium.
Ion exchange is the name of the procedure.
A mineral tank serves as the brain of a water softener.
Small polystyrene beads, sometimes known as resin or zeolite, are used to fill it.
A negative charge is present in the beads.
Both calcium and magnesium have positive charges in water.
As the hard water flows through the mineral tank, these minerals will adhere to the beads.
Positive charges exist on sodium ions as well, however they are not as strong as those on calcium and magnesium.
The sheer amount of sodium ions is sufficient to force the calcium and magnesium ions off the beads when a very strong brine solution is pushed through a tank containing beads already saturated with these ions.
This brine solution is produced in a separate brine tank by water softeners using table salt.
In a typical process, hard water enters the mineral tank, where calcium and magnesium ions replace sodium ions by moving to the beads.
The water is exposed to sodium ions.
A three-phase regenerative cycle is initiated after the calcium and magnesium beads are fully saturated.
In order to flush filth out of the tank, water is first reversed during the backwash phase.
The concentrated sodium-rich salt solution is transported via the mineral tank from the brine tank during the recharge phase.
In place of the calcium and magnesium that are lost in the drain, the sodium builds up on the beads.
After this stage, the surplus brine is drained from the mineral tank, and the brine tank is filled once again.
The Minds
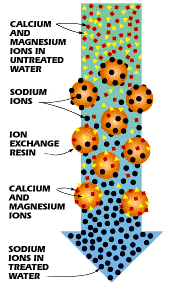
Hard water ions replace sodium ions on beads during ion exchange.
To remove the minerals, the process is turned around.
The majority of widely used water softeners use an automated regeneration mechanism.
The simplest kind features an electric timer that regularly flushes and recharges the system.
Soft water is not accessible while recharging.
A computer-based second form of control monitors the amount of water consumed.
The computer starts regeneration when enough water has gone through the mineral tank to deplete the sodium beads.
These softeners often feature reserve resin capacity, ensuring that there will be some soft water accessible while being recharged.
A mechanical water meter is used in a third form of control to gauge water use and start recharging.
The benefit of this method is that it doesn’t need any electrical components and just recharges the mineral tank when it’s necessary.
Softened water is always accessible when it has two mineral tanks, even while the device is charging.
Evaluation of Water Hardness
Water hardness test kits are often provided by businesses that sell water softening equipment to customers.
Look for “water analysis” in your Yellow Pages to find options for commercial testing.
The hardness of water is expressed in parts per million, or ppm, or in grains per gallon (GPG) or milligrams per liter (mg/L).
Water is categorized as soft up to 1 GPG (about 17.1 mg/L) and moderately hard up to 3.5 GPG (60–120 ppm).
The efficacy of a water softener is influenced by how hard the incoming water is.
Water with a GPG greater than 100 may not soften entirely.
Health Issues
No health risks are posed by hard water.
On the other hand, those on salt-restricted diets could have a problem with the sodium that is still present in softened water.
Others may just want to stay away from the somewhat salty flavor of treated water.
You may install a different water dispenser that skips the softener in either scenario.
In addition, potassium chloride may be used in place of salt, albeit it will cost three to four times as much.