When assessing the components of your solar system, you need consider more than just the solar panels.
Solar power inverters, which transform the energy your solar panels produce into a form that can be utilized by the appliances, lights, and other electronics in your house, play an equally crucial function in a solar system.
The EnergySage Solar Marketplace can assist you in comparing solar bids with various inverter types after you have a basic understanding of how solar inverters operate and the many kinds of inverters available for solar.
Why Would A Solar Inverter Be Used? How A PV System’s Solar Inverters Operate
Direct current (DC) energy is generated when the sun shines on your solar photovoltaic (PV) system, thanks to the movement of electrons within the solar cells.
Cellular circuits gather this energy for usage by you in your house.
Your solar inverter will be useful in this situation.
Your solar panels’ generated energy is useless on its own since most houses utilize alternating current (AC) rather than direct current (DC) electricity.
Your solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, which is then sent to the inverter, which converts the DC energy into AC energy.
Then, if you are creating more solar energy than you need, you may feed it back into the grid or use it to power your devices and appliances.
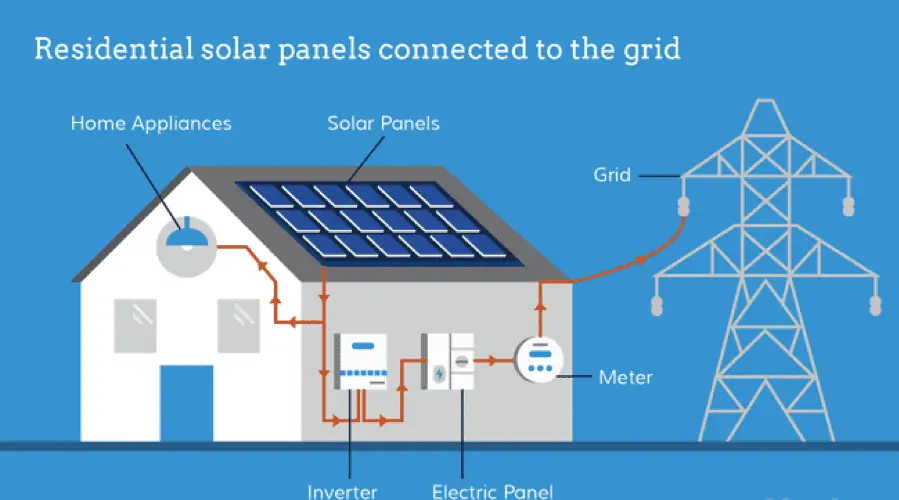
Solar Inverter Technology Comparison: Microinverters Vs. String Inverters Vs. String Inverters With Power Optimizers
The fundamental job of all inverters is to transform DC solar energy into useable AC electricity for your house.
For your solar panel system, you may choose from three distinct solar inverter technologies, and each of them operates a little bit differently.
A Common Centralized Inverter Is A String Inverter.
String inverters, usually referred to as “central” inverters, are typically used in small-scale solar energy systems.
Each panel is hooked into a “string” in a solar PV system with a string inverter, and many strings (often up to three) may be connected to your main inverter.
All of the electricity generated by your panels is transported to a single inverter, which is often situated on the outside of your house, in a garage, or in the basement.
The inverter will transform all of the solar-generated power into AC electricity that may be used on your home.
Pros: String inverters are the most affordable kind of inverter and have a long lifespan.
Because they are in an accessible area, they are also the simplest to maintain.
Cons: The output of each solar panel on a string may be affected if one solar panel’s performance declines (for example, as a result of shade).
Even while an inverter with many strings can support different roof planes, string inverters may not be the best choice for more intricate system designs or roofs with frequent shadowing.
Best for: Households seeking for less expensive solar PV systems and buildings with “uncomplicated” roofs that get steady sunlight throughout the day.
Power Optimizers: A String Inverter And Panel-Located Alternative
A compromise between string inverters and microinverters is what power optimizers are.
Power optimizers are situated on the roof adjacent to (or integrated with) individual solar panels, much as microinverters.
However, power optimizing systems still transfer electricity to a central inverter.
At the location of the solar panel, power optimizers do not transform the DC current into AC electricity.
As an alternative, they “condition” the DC power by adjusting its voltage before sending it down to the string inverter.
In shade conditions, a system that combines power optimizers and a string inverter is more effective than one that does not.
Pros: Power optimizers tend to be less expensive than microinverters, but they may still increase the efficiency of your solar panel system if you have a convoluted roof or often shaded areas.
They provide the advantage of monitoring the performance of individual panels as well as optimizing the output of each individual panel to reduce the potential influence of any one darkened panel.
Cons: Compared to systems with a basic string inverter option, systems that combine power optimizers with a string inverter will be more expensive.
Similar to microinverters, power optimizers in solar PV systems might make maintenance more challenging.
Best for: Homeowners that are prepared to spend extra to improve the performance of their solar panel system but do not want to invest in microinverters and have a little less than optimal roof for solar.
High-Performance Microinverters Come With A Greater Price.
Microinverters are “distributed” inverters if a string inverter is a “central” inverter.
Microinverters are miniature inverters that are positioned at the location of each solar panel in solar PV installations.
Microinverter systems convert the DC solar energy from the panels directly onto the roof, as opposed to transmitting electricity from each panel down to a single inverter.
Pros: Having microinverters at each solar panel enhances performance, particularly for systems with more intricate designs or those that are shaded.
Microinverters enable panel-level system monitoring and minimize the effects of shading by optimizing each panel’s output at the panel level.
Cons: Because they are installed on the roof, microinverters are more expensive than string inverters and may be more challenging to maintain or fix in the case of a malfunction.
Best for: Solar systems with panels facing several directions, homeowners who wish to optimize solar output in a short area, and buildings with “complex” roofs that feature gables, chimneys, or other things that might cast shadow.
Selecting The Ideal Inverter For Your House
The next step is to choose the finest sort of solar inverter for your solar PV system now that you are familiar with how they operate.
It’s not always essential to spend more money on optimizers or microinverters, and not every system design is suitable for string inverters.
In the end, there is only the solution that is optimal for your particular requirements and circumstances.
You may use the following extra materials from EnergySage to decide which solar inverter is best for you:
Contrasting power optimizers, microinverters, and string inverters
- Which panel-level option—microinverters vs.
- Power optimizers—is best for you?
- Power optimizers and microinverters: pros and drawbacks
Visit the EnergySage Buyer’s Guide to view all available solar inverter models and compare inverter attributes like efficiency and warranties.
While you may learn more about the various technologies, it’s preferable to compare real quotations from certified local installers in your region to choose which choice is right for you.
Once your house has been registered on the EnergySage Solar Marketplace, you may explore offers that have been tailored to your residence and compare the advantages and disadvantages of various inverter solutions.
Simply by comparing all of their equipment, financing, and installer choices, customers who compare quotes on EnergySage may save 20% or more on their solar installation.